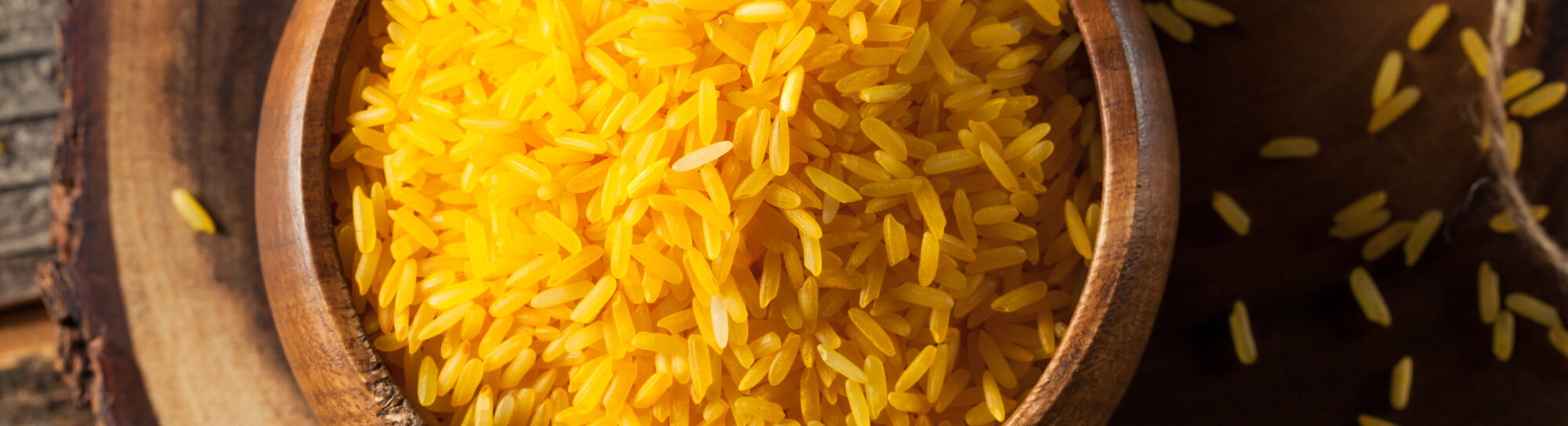

Gene Technology Obstacles Result in Lost Lives
The World Health Organization (WHO) believes that a staggering 500,000 children across the globe become blind every year due to a lack of vitamin A. Alarmingly, about half of these children lose their lives within a year of losing their sight. The tragic toll could have been significantly reduced earlier.
Wednesday, September 20, 2023
A 2014 study in the journal "Environment and Development Economics" found that the delay in introducing Golden Rice has resulted in a loss of approximately 1.4 million life years up to that point. Golden Rice serves as an affordable daily source of nutrition, capable of tackling vitamin A deficiency in impoverished regions. This rice is engineered to enhance the production of beta-carotene, which is a precursor to vitamin A. Its distinctive yellowish tint gave it its name. The brainchild of Professor Ingo Potrykus from ETH Zurich, Golden Rice was conceptualized two decades ago.
The Intense Opposition
Despite its evident benefits, especially for those surviving mainly on a meager meal of one or two bowls of rice daily, Golden Rice has faced significant hurdles. A glimmer of hope emerged last year in the Philippines when farmers were granted permission to cultivate this rice, yielding a pioneering harvest of nearly 70 tons. This groundbreaking moment was short-lived. The nation's Supreme Court has once again halted its cultivation, prompted by a plea from Greenpeace and a local group named Masipag. In spring 2023, the court mandated further confirmation of Golden Rice's safety before granting any permissions.
Backing from the Scientific Community
Over the years, consistent research has vouched for the safety of this genetically modified rice variant. Notably, back in 2016, over a hundred Nobel laureates urged Greenpeace through an open letter to cease their opposition to genetic engineering, particularly targeting Golden Rice. They beseeched the organization to respect and acknowledge the consensus among premier scientific institutions. These institutions have consistently found that genetically engineered foods are as safe, if not safer than conventionally produced alternatives. The poignant question raised in their letter was, "How many more lives need to be lost before we recognize this as a crime against humanity?" The fate of Golden Rice, in the Philippines or elsewhere, remains uncertain in the wake of this judicial decision.
Persistent Pursuits by Scientists
While a balanced diet caters to the array of human micronutrient needs, the grim reality is that vast sections of the world have scarce access even to basic nourishment. For many, a well-rounded diet is nothing but a distant dream. This makes combating micronutrient deficiencies all the more crucial. Enter genetic engineering, with its enormous potential. For instance, in West Africa, cassava, a staple food, meets some of the iron and zinc needs, albeit not adequately. Scientists from the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center in St. Louis, USA, have enhanced its iron content by three to seven-fold using genetic engineering. Navreet Bhullar, a lecturer at the Institute of Molecular Plant Biology at ETH, is improving food plants in terms of their micronutrient content. Bhullar's team has developed transgenic rice varieties that not only accumulate iron and zinc in their grains, but also produce beta-carotene as a precursor of vitamin A. With their multi-nutrient rice, the research group is leading the way. "We developed it with classical genetic engineering because that is not possible with conventional breeding" explains the biotechnologist. Bhullar has not yet worked with Crispr/Cas. However, she sees great potential for sustainable agriculture in the combination of traits such as drought tolerance, pest resistance and micronutrients, which can also solve global food problems. Such innovative strides hold the promise of addressing widespread malnutrition in the future. Unwavering in their belief, these scientists view genetic engineering as a boon for humanity.
Kindly note:
We, a non-native editorial team value clear and faultless communication. At times we have to prioritize speed over perfection, utilizing tools, that are still learning.
We are deepL sorry for any observed stylistic or spelling errors.
Related articles

“Natural does not always mean sustainable”
We are reliant on optimized foodstuffs in order to supply the planet’s growing population with healthy, sustainably produced food. However, consumers often view these as “artificial”, and thus “unnatural” – and “natural” is the preferred choice. Of our everyday foods, however, very few are of “natural origin”. They have been optimized by humans over the course of time. But are supposedly “natural” products also healthier and more sustainable? Three presenters took an in-depth look at food optimization in this Swiss-Food Talk.
Proven innovation protection and continued freedom for breeders
No European country applies for more patents per capita than Switzerland. Patent protection is a mandatory prerequisite for research and development, a foundation of Swiss welfare.

The great benefits of biotechnology in agriculture
Bioengineered crops have been cultivated in many parts of the world for around 25 years. Several publications bear witness to the great benefits of biotechnology in agriculture. The cultivation of the plants has a positive effect on the environment, the climate and yields for farmers.

How our daily lives end up in the water
When residues in our waters are discussed, agriculture is often portrayed as the main culprit. Yet a closer look shows that the sources are diverse and often much closer to everyday life than assumed.

New Breeding Methods at a Crossroads
It will soon become clear whether plants developed through modern genomic breeding techniques will be allowed to be cultivated in European fields in the future. Switzerland in particular would be well advised to at least keep an eye on decisions made in Brussels in order not to fall behind.

Why Strict GMO Regulation Stifles Innovation
New breeding techniques such as CRISPR-Cas are considered key to developing resilient crops, stable yields and reducing the need for plant protection products. ETH professor Bruno Studer warns that overregulating these technologies strengthens precisely those large agricultural corporations that critics seek to curb, while excluding smaller breeders and start-ups from the market.

A Superfood with Benefits and Challenges
Sweet lupin is Biovision’s “Superfood of the Year 2026.” It delivers high protein content, improves soils and supports biodiversity. Yet a closer look at agricultural practice shows that without breeding, crop protection and innovation, even this superfood remains a challenging crop.

