
On the trail of POISONs
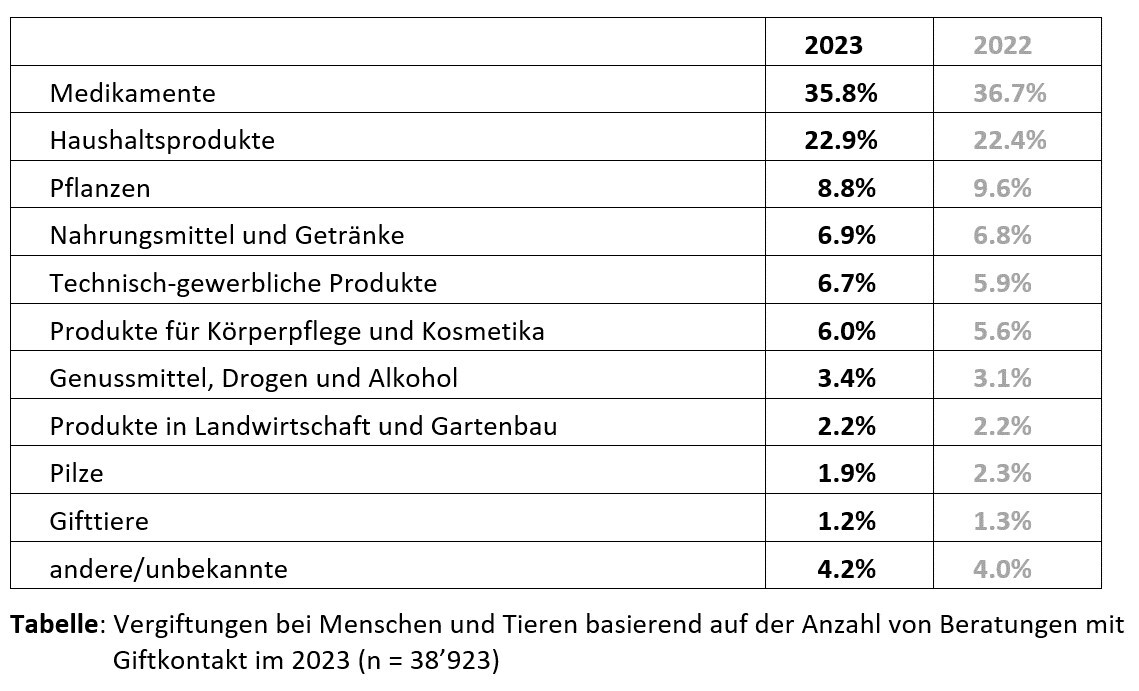
New 2023 data from Tox Info Suisse shows: Medicines and household products are primarily responsible for poisonings in Switzerland. Tox Info provided over 40,000 telephone poison counselling sessions last year. The statistics contrast with the media coverage. When the media talk about "poison", the focus is usually on pesticides. In the consultation statistics, however, products from agriculture and horticulture figure towards the bottom of the table with 2.2 per cent of consultations.
Friday, January 26, 2024
"With 41,261 consultations, poison counselling was used 1.7% more frequently than in the previous year. As is the case every year, a good 40% of enquiries related to children of pre-school age, which typically involve accidents. For adolescents (around 5% of all calls), on the other hand, the focus is on intentional poisoning, especially suicide attempts and, to a lesser extent, substance abuse," writes Tox Info Suisse in a press release. Radio SRF has also reported on this. (4:29)
The poisoning counselling statistics are also consistent with statements by experts. The German veterinary surgeon and microbiologist Andreas Hensel, for example, showed in a remarkable interview with the Berlin Tagesspiegel how misguided people's perception of the risks associated with pesticides is. Hensel has been the first president of the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment in Berlin, which analyses the safety of chemicals, since 2003. A particular focus is on consumer protection. Hensel recently coined the phrase in the FAZ: "Most people don't die from things they are worried about."
The statistics from Tox Info Suisse contrast with many media reports on the subject of crop protection, where there are constant warnings about poison in food. Hensel also told the FAZ: "In Germany, the fear of so-called chemicals in food is particularly high. Yet our food is safer than ever before. In our everyday lives, we constantly come into contact with potentially dangerous situations or substances. Despite this, there is not necessarily a risk to our health. There is no evidence in Germany that anyone has been poisoned by food containing crop protection residues. This is shown by the evaluations of the German poison information centres. Nevertheless, the scaremongering narrative of toxic crop protection residues has been used regularly for decades."
Good to know:
Chemophobia refers to a panicky fear of chemicals. In contrast, the natural world is seen as the source of all good things. From a scientific point of view, this simplified view is nonsense. Synthetic is not synonymous with toxic, as laypeople often think. The dose is decisive for the toxicity of both natural and synthetic substances.
Kindly note:
We, a non-native editorial team value clear and faultless communication. At times we have to prioritize speed over perfection, utilizing tools, that are still learning.
We are deepL sorry for any observed stylistic or spelling errors.
Sources
Related articles

Residue is not the same as residue
Painkillers like Voltaren are a blessing for us – yet in our rivers they can harm fish. If these were crop protection products, calls for bans would be immediate. It becomes clear that we are applying double standards.

ARTE documentary: Genetic engineering in organic farming?
The ARTE documentary “Genetic engineering in organic farming?” examines key controversial questions of modern agriculture: Is the general exclusion of new breeding technologies still up to date? Can the resistance of organic farming be justified scientifically?

The Great Suffering of Farmers
Fire blight, Japanese beetles, or grapevine yellows – farmers in Valais, too, are increasingly feeling helpless in the face of the threats posed by nature. More and more often, they lack the means to effectively protect their crops. This makes it all the more important for the Federal Council to place a pragmatic balancing of interests at the forefront when setting threshold values.

'Tomatoes on your eyes'
The submitted “Food Protection Initiative” calls for “GMO-free food.” Leaving aside this illusory demand, its adoption would mean more bureaucracy, more trade barriers, and less innovation. The Swiss Farmers’ Union describes the proposal as “unnecessary” and warns of a setback to the goal of achieving an even more sustainable agriculture.

